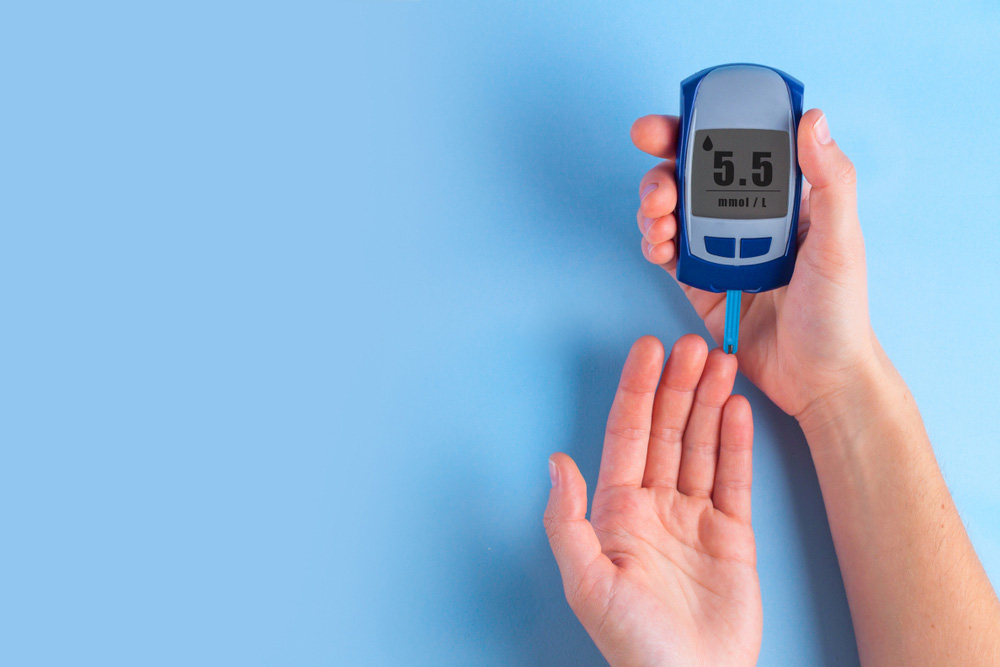
Type 1 English – What is Diabetes?
Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. High blood sugar problem starts when your body no longer makes enough of a chemical, or hormone, called insulin. Your body changes much of the food that you eat into a type of sugar called glucose. This sugar travels in your blood to all the cells in your body. Your body cells need the sugar to give you energy. Insulin helps sugar to move from your blood into your cells. Without insulin, your cells can’t get the sugar they need to keep you energetic. By moving sugar from your blood to your body cells, insulin helps to keep your blood sugar level normal (not too high; not too low). When you don’t have enough insulin to lower high blood sugar levels means you have diabetes. High blood sugar levels can cause serious health problems Diabetes can, and must, be treated.

Type 1 English – When you have Diabetes?
Your body does not make insulin at all Your body does not make enough insulin, or the insulin that body makes doesn't work right. Blood sugar levels stay high of you doesn’t have enough insulin to move sugar from your blood into your cells.

Type 1 English – Type 1 Diabetes
In this type 1 diabetes, the body cannot make insulin. Type 1 diabetes occurs more often in the children and young adults than in older adults. People with type 1 diabetes must inject insulin to control their blood sugar.

Type 1 English – Symptoms of type 1 diabetes
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- A fruity-like smell
- Fatigue weakness
- Sugar in urine
- Excessive weight loss

Type 1 English – Complications of diabetes
- Heart attacks and stroke
- Kidney problems
- Numbness in the feet and sores that don’t heal
- Vision problems
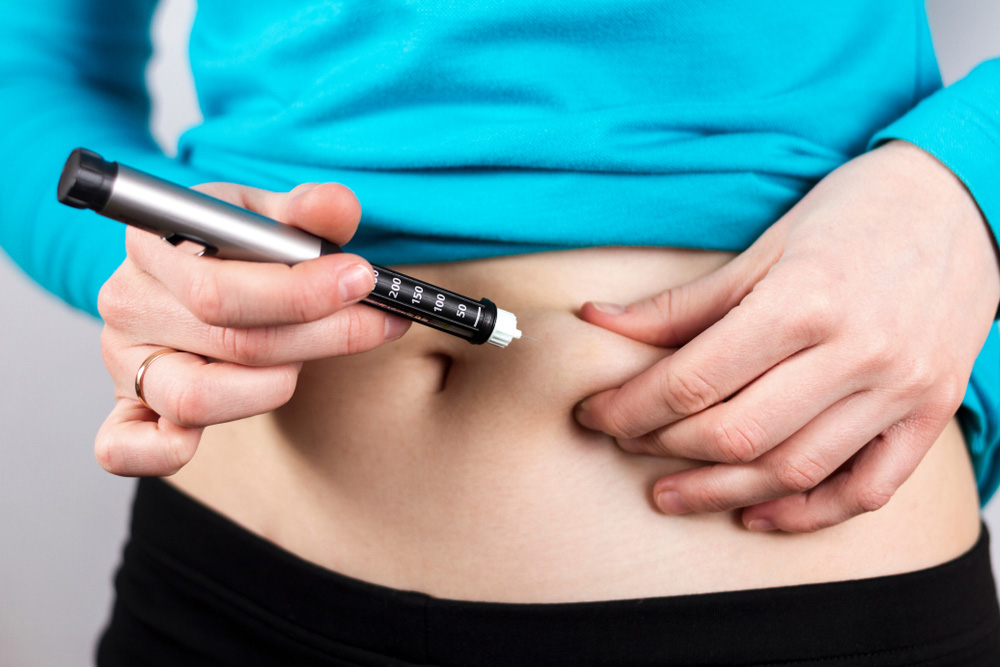

Type 1 English – Why do I need Insulin?
It is a hormone produced by pancreas to regulate the levels of glucose in the blood. In absence of insulin our body cells cannot use glucose as a source of energy. When you have diabetes, your body doesn’t make insulin or the insulin you do make doesn’t work right. Hence, you need external insulin. You can get the insulin you need by injecting it with an insulin pen, a syringe, or insulin pump. Taking insulin will: Help you to control your sugar levels Give you energy Help you to stay healthy

Type 1 English – Insulin Secretions in Body
Insulin is secreted during fasting state known as Basal Insulin. The secretion of insulin increases in response to increased blood glucose levels after taking food. This process is affected in diabetes for which insulin from outside needs to be injected.
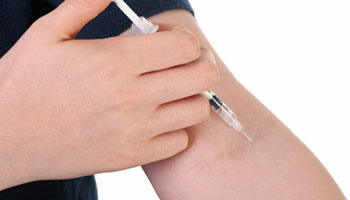
Type 1 English – How should I take Insulin?
Insulin works best when you inject it into the fatty parts of the body just under the skin. Before you leave the clinic, ensure that you know how to: Prepare insulin Inject insulin Rotate injection site
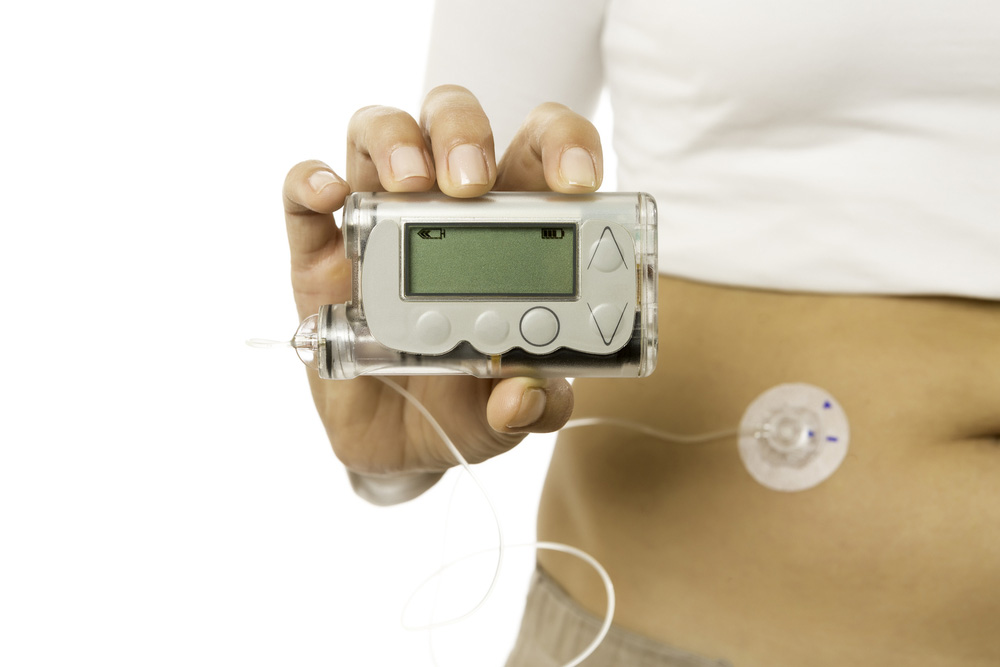
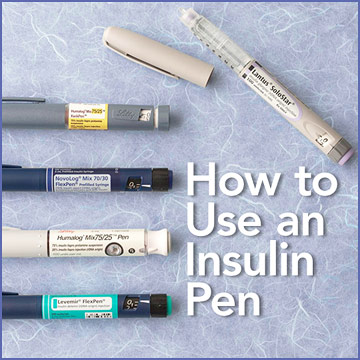
Type 1 English – Which are the insulin delivery devices?
There are different devises to deliver insulin into your body through; syringes, insulin pen, insulin pump, and i-Port are different options for insulin delivery.
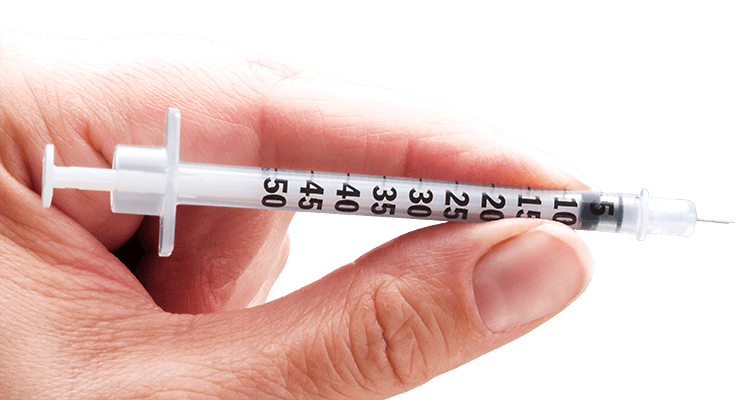
Type 1 English – Syringe
Insulin syringes are different from normal one. They are thinner, have almost pain less needle and come with removable needle guard. The outer side of the syringe is marked with lines to assist you to withdraw correct amount of insulin.
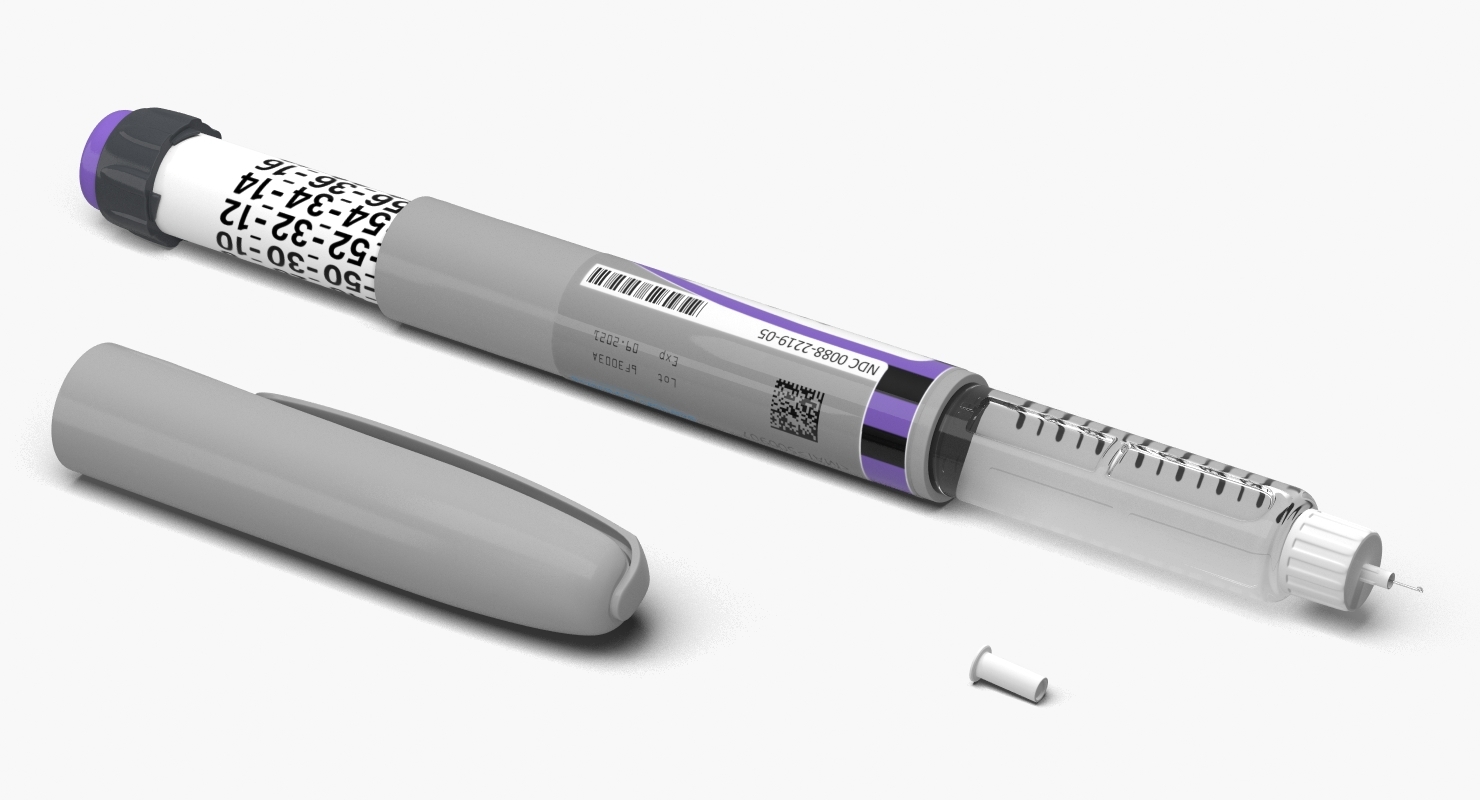
Type 1 English – Pen
It is composed of an insulin cartridge (integrated or bought separately) and a dial to measure the dose, and is used with disposable pen needles to deliver the dose. Insulin pens offer several significant advantages over insulin syringes: Ease of handling
Type 1 English – How to inject using a syringe?
Wash hands with warm & soapy water If using cloudy insulin, roll the bottle (do not shake) between hands. Clean rubber stopper of insulin bottle with alcohol. Fill syringe with air equal to the number of units of insulin you will be taking. Insert needle into the bottle and push air into the insulin bottle. Turn syringe and bottle upside down and draw out your dose of insulin. Insert the needle into the skin Press the plunger on the end of the syringe to deliver the dose
Type 1 English – How to inject using a pen?
Screw or click on a new pen needle. If necessary, prime the pen to remove any air from the needle Turn the knob on the end of the pen (or "dial") to the number of units needed Insert the needle into the skin Press the button on the end of the pen to deliver the dose Count to five or ten depending on dose injected Remove used pen needle for disposal

Type 1 English – Some tips for using the syringe and Pen for insulin delivery
Shorter needles mean lesser injection discomfort. However, injection depth affects how quickly insulin takes effect. Coordinate syringe size (e.g., 1cc, 1/2cc, 3/10cc) to match insulin dose. Do not re-use a syringe/pen needle. Do not share a syringe. Dispose of used syringes/ pen needle properly
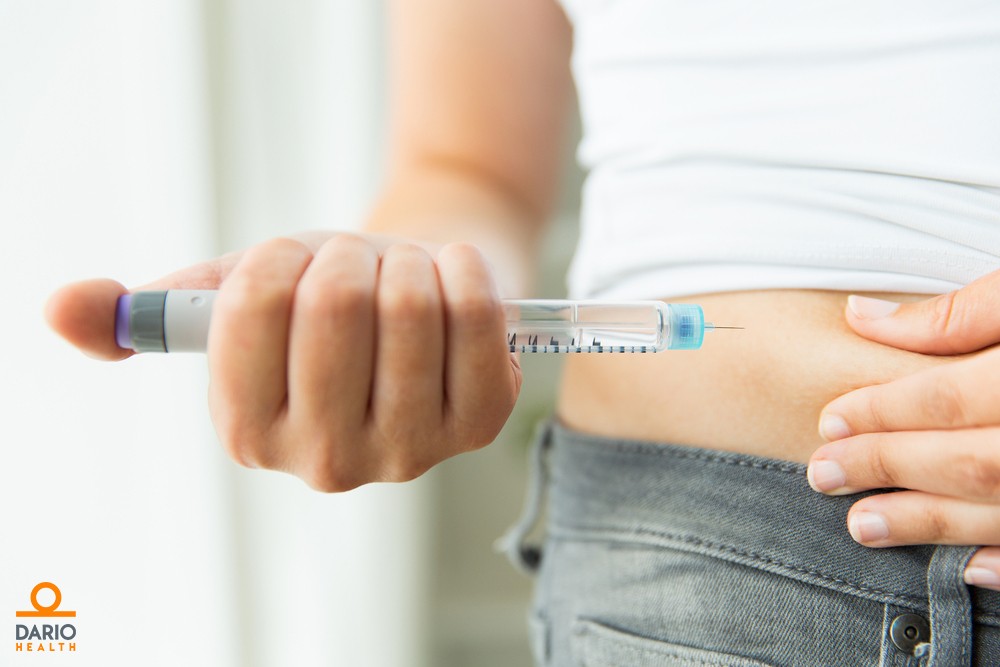
Type 1 English – Where Should I inject insulin?
Insulin works best when you inject it into the fatty parts of the body just under the skin.
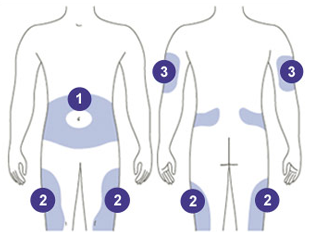
Type 1 English – Following are insulin injection sites
Back of upper arms Stomach (around navel) Front and side area of thighs Back above waist Rear end (buttocks) Keep 1 inch away from the last few injection sites. Keep 2 inches away from the navel and any scars. Do not use sites that are bruised, tender; swollen or hard to the touch.
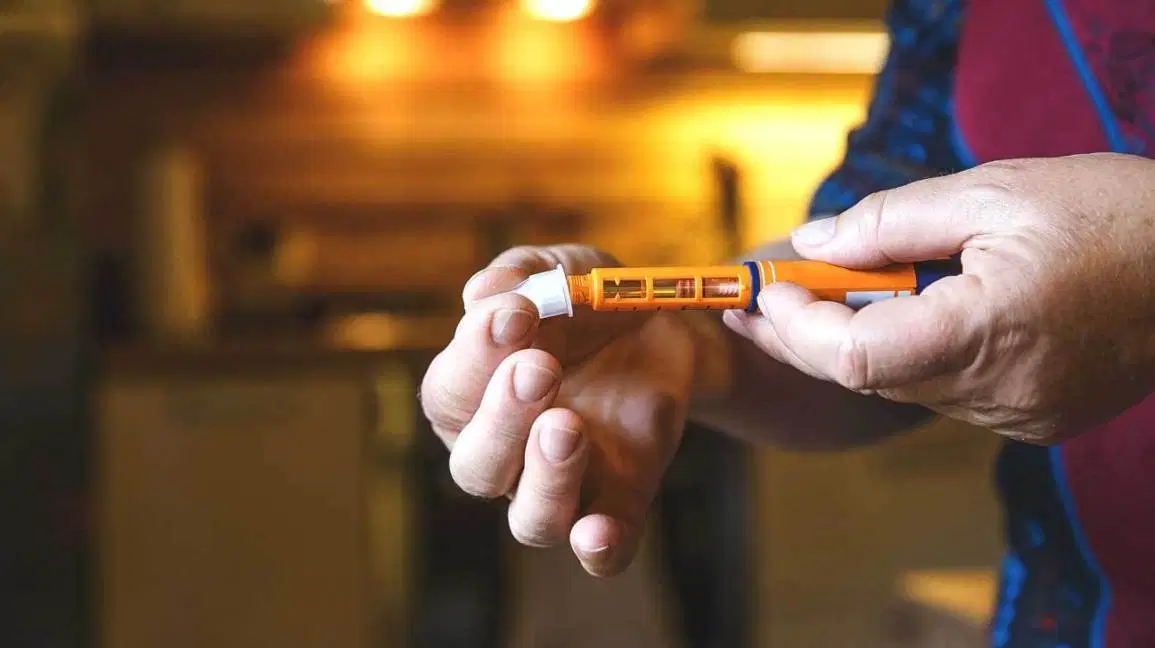

Type 1 English – Things to note while choosing site of injection
Rotation of the injection sites may reduce the risk of lipodystrophy, lumps of fat that develop under the skin from injecting in the same spot repeatedly. Two rules for proper site rotation Same general location at the same time each day Rotate within each injection site
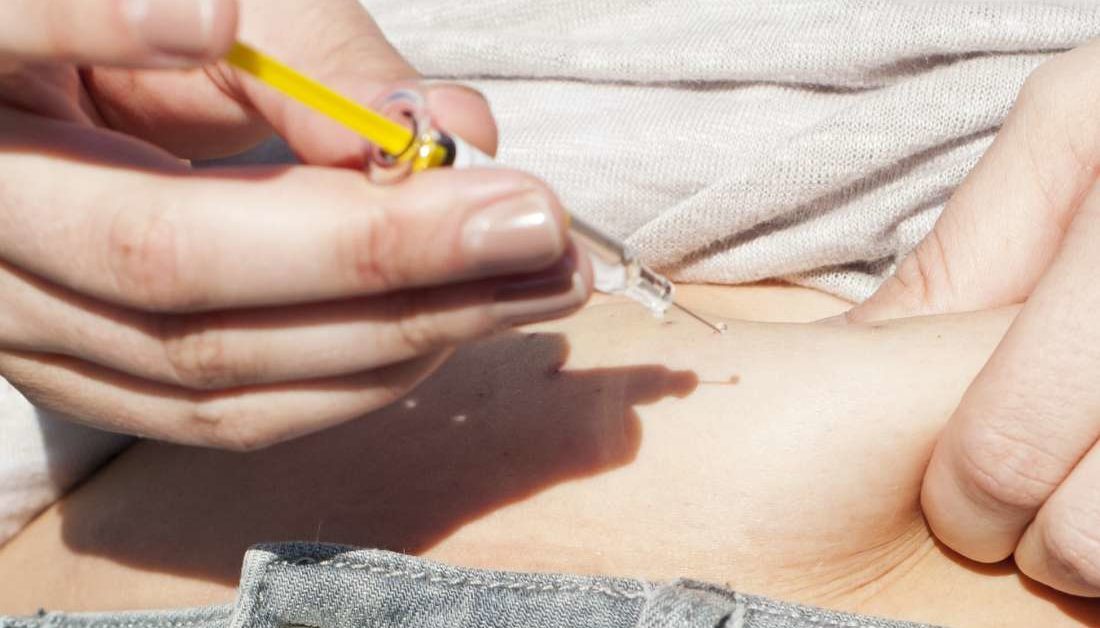
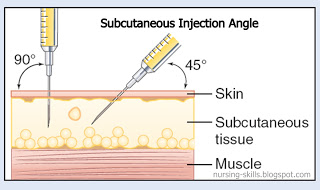
Type 1 English – Angle of injection and Skin folding
Most people pinch up a fold of skin and insert the needle at a 90° angle to the skin fold. To pinch your skin properly, follow these steps: Squeeze a couple of inches of skin between your thumb and two fingers, pulling the skin and fat away from the underlying muscle. (If you use a 4 or 5 millimeter mini pen needle to inject). Insert the needle. Hold the pinch so the needle doesn't go into the muscle. Push the plunger (or button if you're using a pen) to inject the insulin. Release the grip on the skin fold. Remove the needle from the skin.